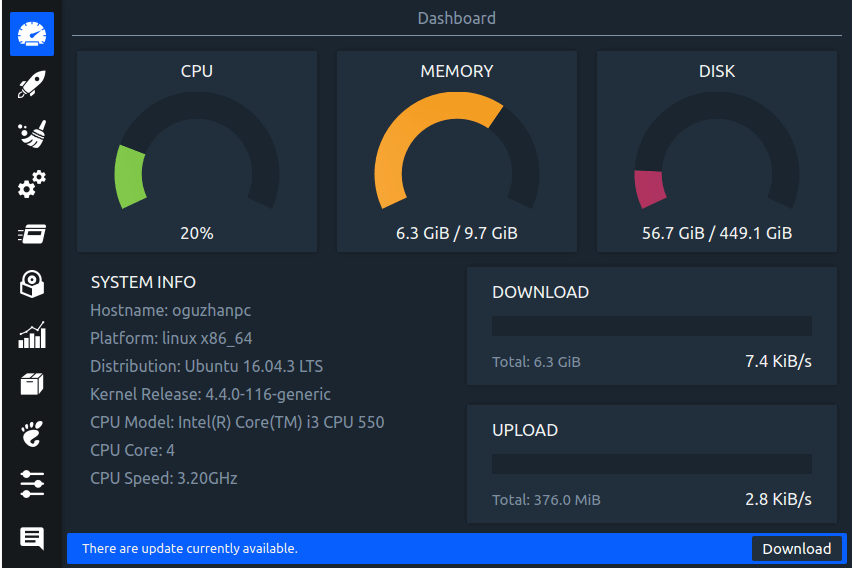
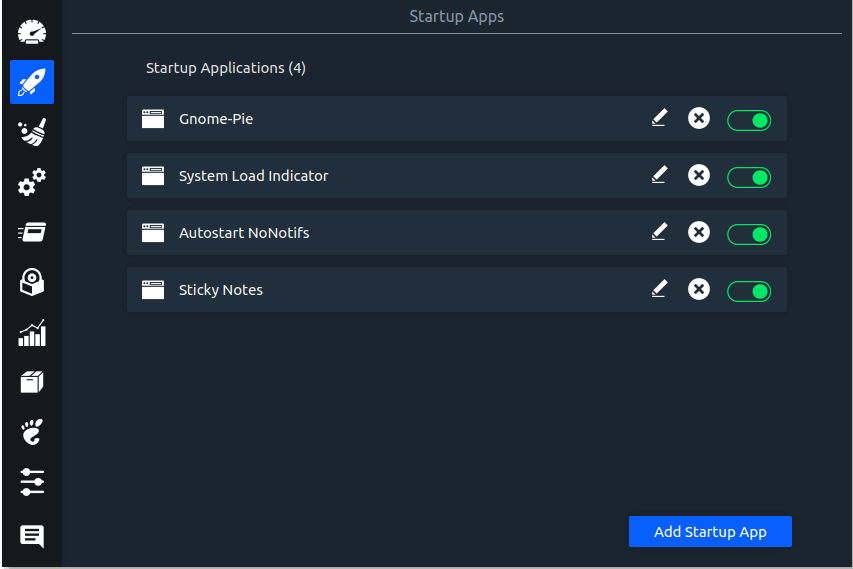
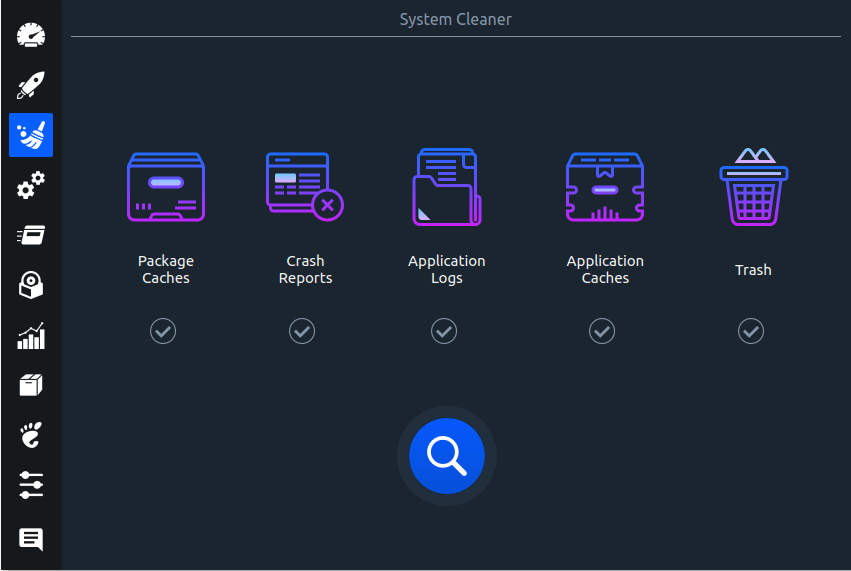
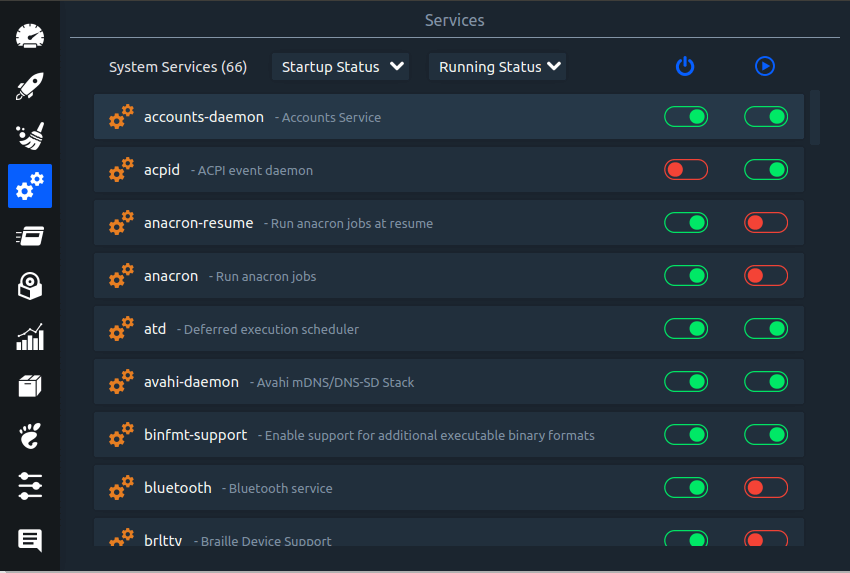
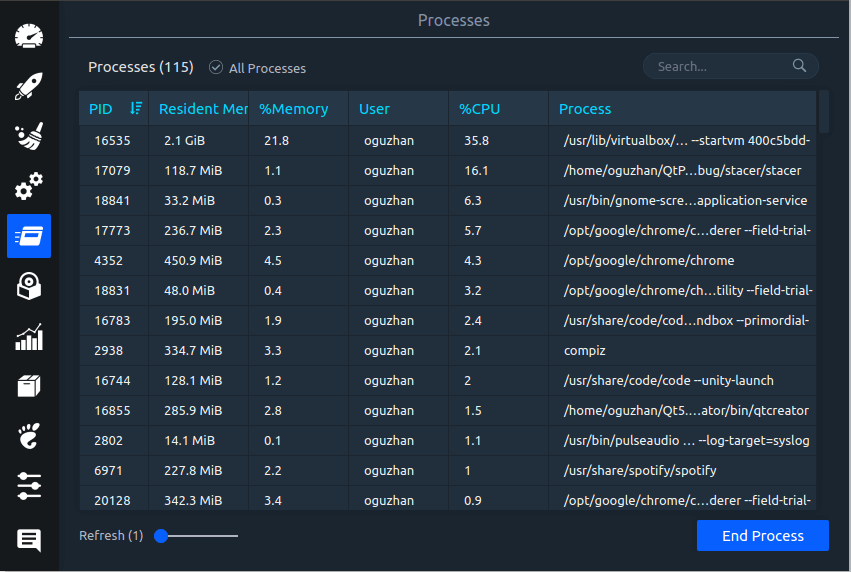
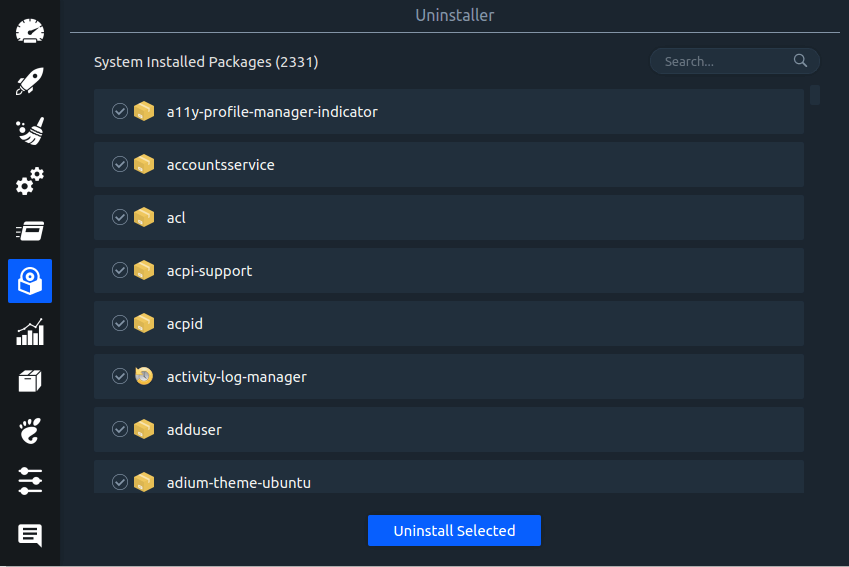
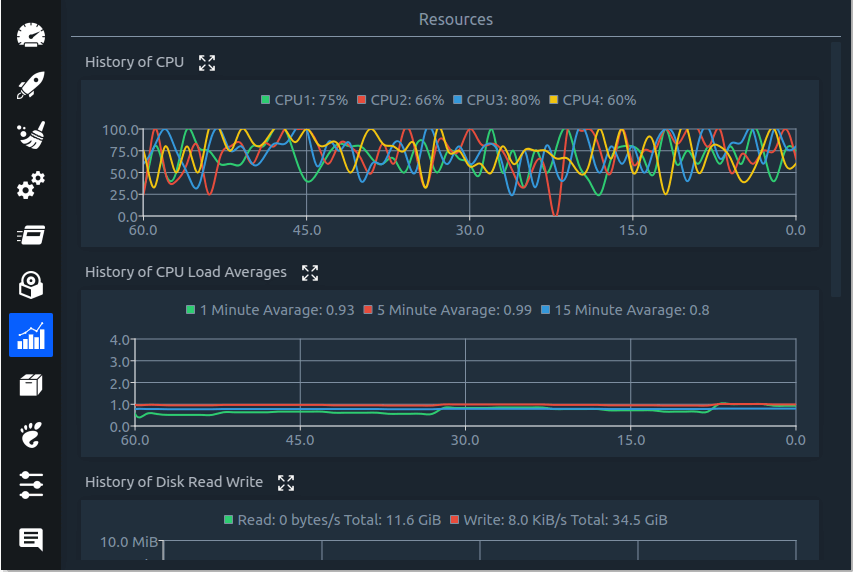
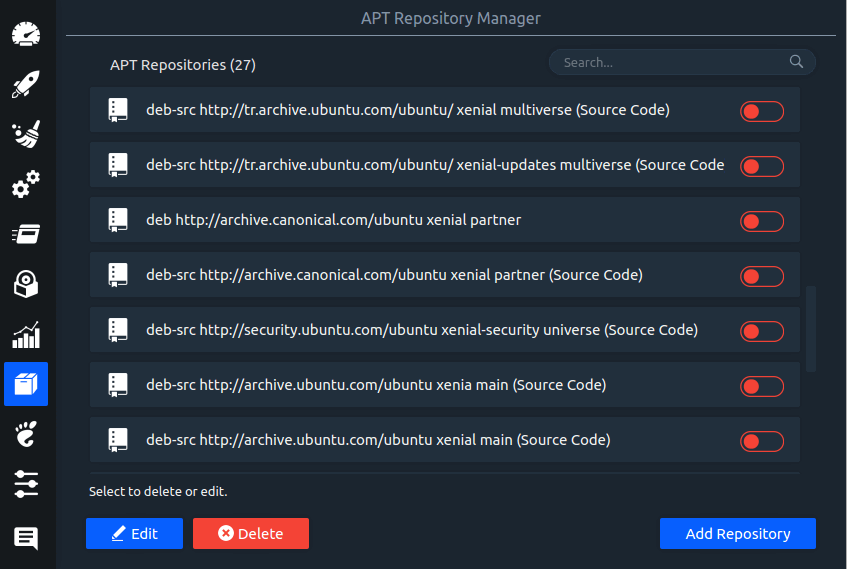
Linux System Optimizer & Monitoring
Stacer is an open source system optimizer and application monitor that helps users to manage entire system with different aspects, its an all in one system utility.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:quentiumyt/stacer
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install stacer